I will show what I entered in the calculator and what it gave me back!
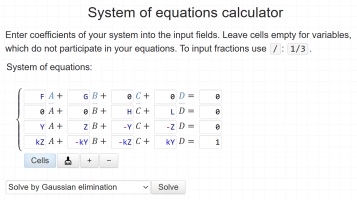
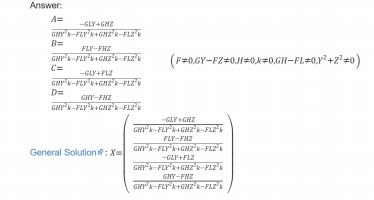
And it gave me this solution:
\(\displaystyle A = \frac{\sin ka\sin k(b-x)}{k\sin k(b - a)}\)
Let us take, for example, \(\displaystyle A\) from the calculator and simplify it to see if it matches the above.
\(\displaystyle A = \frac{-GLY + GHZ}{GHY^2k - FLY^2k + GHZ^2k - FLZ^2k}\)
\(\displaystyle = \frac{G(HZ - LY)}{(GH - FL)kY^2 + (GH - FL)kZ^2}\)
\(\displaystyle = \frac{G(HZ - LY)}{(GH - FL)(kY^2 + kZ^2)}\)
\(\displaystyle = \frac{G(HZ - LY)}{k(GH - FL)(\cos^2 kx + \sin^2 kx)}\)
\(\displaystyle = \frac{G(HZ - LY)}{k(GH - FL)(1)}\)
\(\displaystyle = \frac{G(HZ - LY)}{k(GH - FL)}\)
\(\displaystyle = \frac{\sin ka(\cos kb \sin kx - \sin kb \cos kx)}{k(\sin ka \cos kb - \cos ka\sin kb)}\)
\(\displaystyle = \frac{\sin ka\sin k(x - b)}{k\sin k(a - b)}\)
\(\displaystyle = \frac{\sin ka\sin k(b - x)}{k\sin k(b - a)}\)
Which matches the first result below:
If I solve this systems of equations, I get:
\(\displaystyle A = \frac{\sin ka\sin k(b-x)}{k\sin k(b - a)}\)
\(\displaystyle B = -\frac{\cos ka\sin k(b-x)}{k\sin k(b - a)}\)
\(\displaystyle C = -\frac{\sin kb\sin k(x-a)}{k\sin k(b - a)}\)
\(\displaystyle D = \frac{\cos kb\sin k(x-a)}{k\sin k(b - a)}\)


